
Structure and functions of 3 types of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the most abundant type of biological molecules.
Monomers of carbohydrates, monosaccharides, are simple sugars, and their primary role is to provide energy. For example, the brain requires a constant supply of sugar to meet its energy needs.
Structural elements of the cell walls in plants and bacteria and cell to cell communications depend on complex carbohydrate polymers such as oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
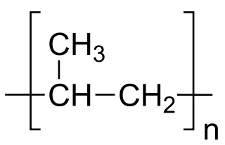
Different types of synthetic polymers and their uses. Addition vs. condensation polymers.
A polymer is a very large molecule that is built from monomers (the repeating units that make up a polymer).
Many different biomolecules, such as DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates, are polymers.
CRISPR companies working with CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technology
Owing to CRISPR/Cas9 technology, speedily expanding gene editing field spawned a lot of CRISPR companies.
5 key PCR components and their functions
5 standard PCR components play crucial roles in DNA amplification.
The polymerase chain reaction requires a set of appropriate oligonucleotide primers, DNA template and polymerase, a buffer and deoxynucleotides (dNTPs).
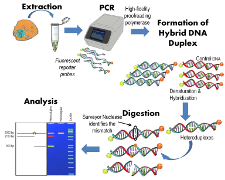
3 basic PCR steps of DNA amplification process
PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction which is one of the fundamental methods of molecular biology.
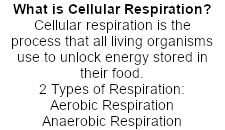
4 main steps of cellular respiration
Metabolic pathways that contribute to the production of ATP molecules in cells are collectively referred to as cellular respiration.
Page 1 of 2